- Understand Opportunistic TLS and Email Encryption: A Deep Dive into S/MIME, Purview Message Encryption, and Secure Email.
- Boosting Email Security with SMTP DANE and DNSSEC: A Complete Guide
Enhancing Email Security: Opportunistic TLS and Encryption Solutions
In Part 1 of this series, we explored how SMTP DANE and DNSSEC collaborate to secure email communications in Exchange Online, ensuring authenticity and encryption between servers. In this follow-up, we focus on two critical components of email security: Opportunistic TLS and email encryption. Specifically, we’ll examine S/MIME and Microsoft Purview Message Encryption, highlighting their key differences, benefits, and use cases.
As businesses face growing cyber threats, protecting sensitive information through robust email security is more vital than ever. By the end of this article, you’ll better understand how these technologies enhance communication security and where they fit into your organization.
Addressing Common Questions About Email Security
After Part 1, several questions emerged, particularly around the fears and uncertainties regarding enabling security features like DNSSEC and SMTP DANE. Questions like, “What happens to legacy systems?” and “How does usability balance with security?” prompted this deeper dive into Opportunistic TLS, a technology designed to maintain usability while improving security.
What is Opportunistic TLS?
Opportunistic TLS enables email servers to establish secure connections using Transport Layer Security (TLS) without prior configuration between sender and recipient servers. If both servers support TLS, the email is encrypted during transmission. However, if the recipient server doesn’t support TLS, the email is sent in plain text.
This approach ensures emails are encrypted when possible but prioritizes delivery over encryption if the recipient server isn’t equipped for secure communication.
How Opportunistic TLS Works
- DNS Lookup: The sending server queries DNS records (MX, A, and AAAA) to locate the recipient’s mail server.
- TLS Negotiation: If the recipient server supports TLS, the connection is encrypted.
- Fallback: If TLS isn’t supported, the email defaults to plain text.
Opportunistic TLS serves as a fallback mechanism, especially when stronger security measures like DNSSEC or DANE validation aren’t available. It prioritizes usability and ensures message delivery, even in less secure conditions.
To better understand how Opportunistic TLS functions, take a good look at the below flowchart. The process begins with an email being sent from a server. The email server queries DNS records, including MX, A, and AAAA records, to identify where the email should be sent. If the domain does not have DNSSEC enabled or a TLSA record present, the server defaults to using Opportunistic TLS, assuming TLS is supported by the receiving server.
As the flowchart shows, Opportunistic TLS is the fallback mechanism used when more robust methods like DNSSEC and DANE validation are not available. This allows email to flow securely when possible but ensures that it is still delivered even when the ideal security conditions aren’t met.
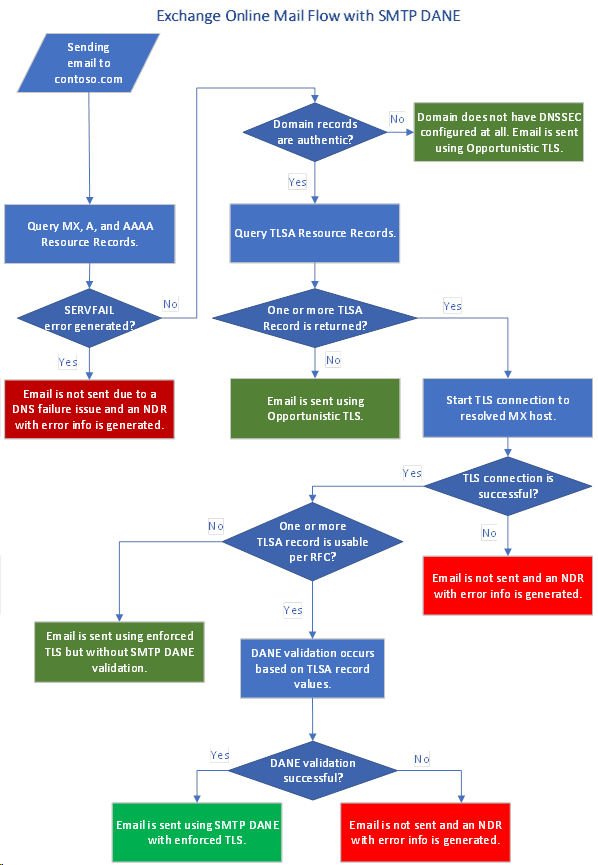
Security Trade-offs of Opportunistic TLS
While Opportunistic TLS offers basic encryption, it lacks mechanisms to verify the recipient server’s authenticity. This vulnerability exposes email communications to downgrade attacks, where an attacker forces emails to be sent in plain text, potentially exposing sensitive data.
For enhanced security, organizations should consider enforced TLS or DANE validation, which offer stricter encryption and authentication guarantees. The trade-off between usability and security is a key consideration when deploying these protocols.
End-to-End Encryption: A Closer Look
End-to-end encryption solutions like S/MIME and Microsoft Purview Message Encryption provide more robust security compared to Opportunistic TLS. Here’s how they work and where they’re best applied.
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)
What is S/MIME?
S/MIME is a certificate-based encryption protocol that uses digital certificates to sign and encrypt emails. It ensures both the authenticity of the sender and the confidentiality of the message content.
How it Works:
- The sender encrypts the email using the recipient’s public key.
- The recipient decrypts the email with their private key.
- Digital signatures verify the sender’s identity and ensure the email hasn’t been tampered with.
Benefits of S/MIME:
- Authentication: Ensures the sender’s identity.
- Integrity: Verifies the email content hasn’t been altered.
- Confidentiality: Encrypts the email so only the recipient can access it.
Use Cases:
S/MIME is ideal for industries like government, legal, and finance, where sender verification and message confidentiality are critical.
Microsoft Purview Message Encryption
What is Microsoft Purview Message Encryption?
Microsoft Purview is a cloud-based encryption solution built on Azure Rights Management (RMS). It simplifies secure communication, particularly with external recipients, without requiring certificate management.
How it Works:
- Emails are encrypted automatically based on predefined rules in Exchange Online.
- Internal recipients in Microsoft 365 can view encrypted emails directly.
- External recipients access encrypted emails through a secure web portal or wrapper email.
Key Features:
- Ease of Access: No certificates required; external recipients can view messages seamlessly.
- Custom Rules: Admins can enforce encryption based on keywords or sensitive information.
- Advanced Controls: Features like message expiration and revocation enhance control over email security.
- Universal Compatibility: Works across platforms like Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook.
Use Cases:
- External Communication: Ideal for securely sharing sensitive information with clients, partners, or contractors.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets data protection requirements like GDPR and HIPAA.
Comparing S/MIME and Microsoft Purview Message Encryption
| Feature | S/MIME | Microsoft Purview |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Strong digital signature-based sender verification. | Relies on organizational policies; no individual certificates needed. |
| Ease of Use | Complex, requires managing certificates. | Simple, works seamlessly for recipients. |
| Key Management | Public-key cryptography, with user-specific certificates. | Centralized management via Azure RMS. |
| Best Use Case | Internal communications with high security requirements. | External communications needing ease of use and flexibility. |
| Advanced Features | Not applicable. | Message revocation, expiration policies, and advanced templates. |
Conclusion
Both S/MIME and Microsoft Purview Message Encryption play essential roles in securing email communications. While S/MIME is suited for internal communications requiring strong authentication, Microsoft Purview excels in simplifying secure external communications without sacrificing usability.
When combined with foundational security protocols like Opportunistic TLS and DANE, these encryption solutions create a comprehensive security framework. By understanding these technologies, organizations can better protect sensitive information, meet compliance requirements, and maintain trust in their communications.



